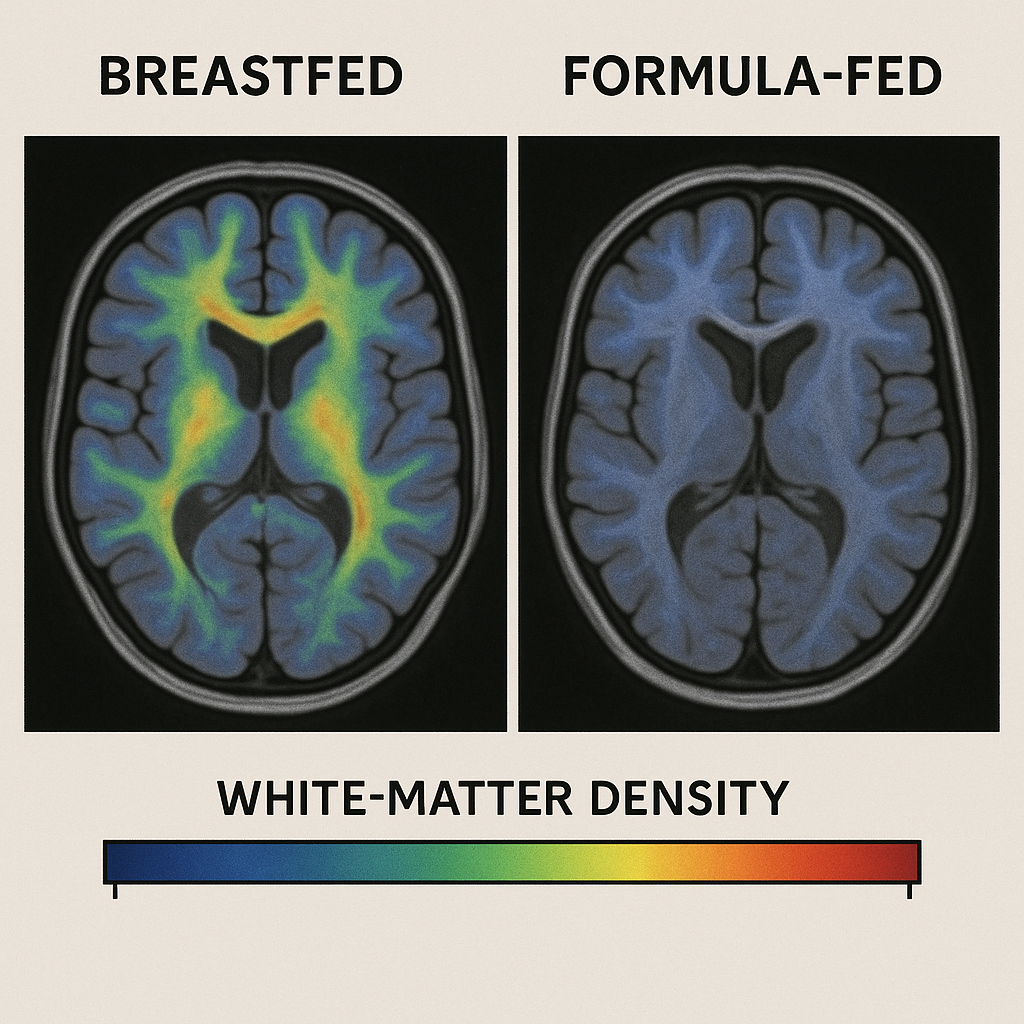
Wondering if breastfeeding can truly make a difference in your baby’s brain development? Research shows that exclusively breastfed babies can have up to 30% more white-matter growth in their brains, as seen in MRI scans Brown University Study. This exciting finding, backed by decades of studies, offers reassurance to parents and practical ways to support their child’s cognitive growth. Below, we dive into the science and share actionable tips to help you nurture your baby’s brain, whether you breastfeed exclusively or not.
- What evidence proves breastfeeding sharpens infant cognition better than formula?
- How do breast milk’s unique nutrients and bio-actives build smarter brains?
- Where does current research fall short—and what should parents do right now?
- Research Gaps:
- Practical Steps for Parents:
- Your Top Questions, Answered
- So, does breastfeeding really boost your baby’s brain?
What evidence proves breastfeeding sharpens infant cognition better than formula?
Multiple studies, including MRI scans, IQ tests, and large cohort research, suggest that breastfeeding offers a cognitive advantage over formula-only feeding, particularly when done exclusively.
- The PROBIT trial, a large randomized study, found that hospital policies promoting exclusive breastfeeding led to a 7.5-point increase in verbal IQ by age 6.5 (PROBIT Follow-Up).
- A Korean study showed children breastfed for 12 months or more scored 6–8 points higher on the Mental Development Index from ages 1 to 3.
- Each month of exclusive breastfeeding is associated with about 0.8 IQ points, indicating a dose-response relationship as per NBC News Report.
- Meta-analyses report a 3–5-point IQ advantage for breastfed children, even after adjusting for maternal education and income.
- MRI research from Brown University found 20–30% more myelinated white matter in breastfed toddlers, especially in regions tied to language and emotional regulation.
For a fuller side-by-side look at feeding methods, visit Breast Milk vs. Formula: What’s Best for Baby’s Brain?.
How do breast milk’s unique nutrients and bio-actives build smarter brains?
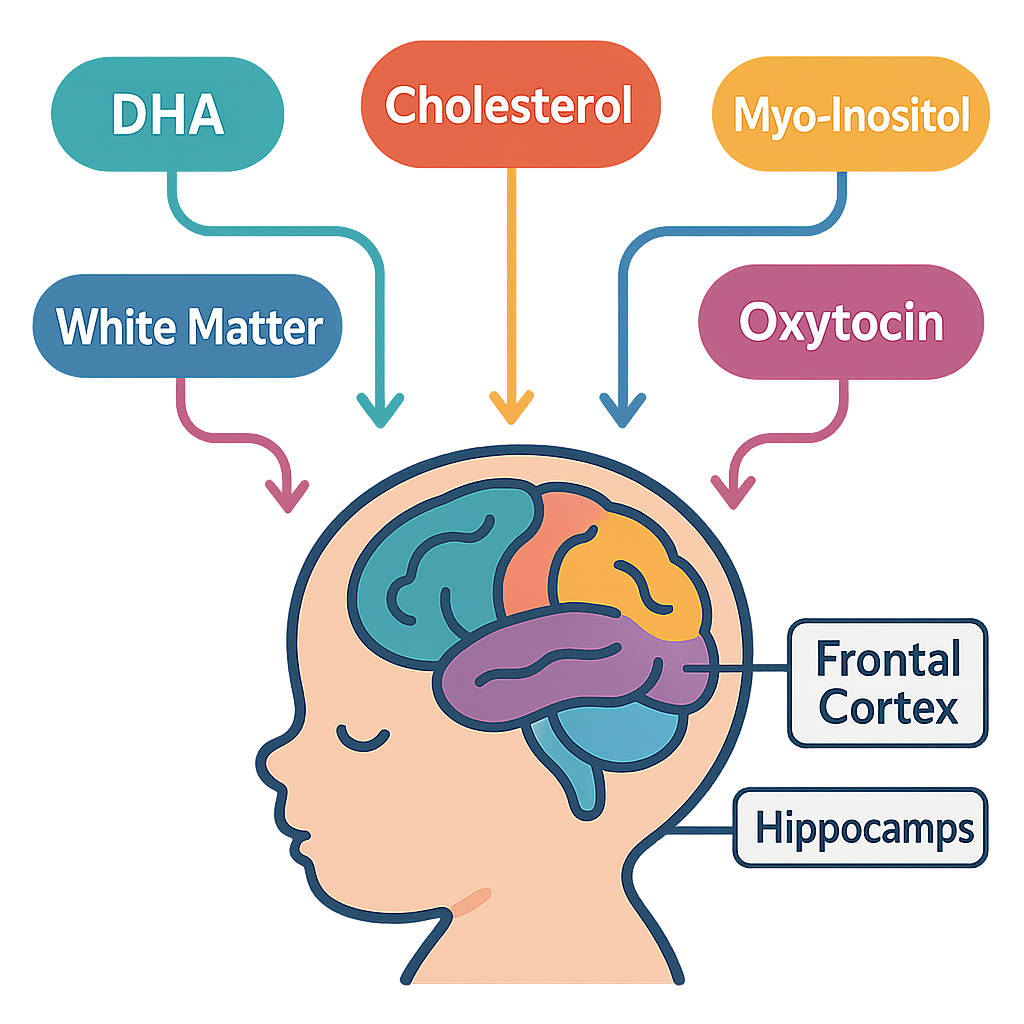
Breast milk is more than just food—it’s a tailored neurodevelopmental toolkit that supports the newborn brain’s growth. Its unique nutrients and bio-actives work together to build neural connections and promote synaptic pruning, essential for efficient brain function. Key components include:
- DHA & ARA – These omega-3 and omega-6 fats speed up myelination, insulating nerve fibers for faster brain communication. Learn more at DHA and Omega-3: Why They’re Key for Your Baby’s Brain.
- Cholesterol + Choline – These strengthen synapse membranes, ensuring quick and efficient neural signals.
- Myo-inositol – A sugar abundant in early milk enhances synapse formation by about 25% in lab studies.
- Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs) – These sugars feed beneficial gut bacteria, which produce metabolites linked to higher cognitive scores, showcasing the gut-brain connection.
- Oxytocin Surge – Nursing triggers oxytocin release, wiring social-emotional circuits that support language and learning.
This combination fosters robust neural networks, setting the stage for long-term cognitive health.
Where does current research fall short—and what should parents do right now?
While the evidence for breastfeeding’s cognitive benefits is strong, some research gaps remain. Parents can still take practical steps to support their baby’s brain development, even if exclusive breastfeeding isn’t an option.
Research Gaps:
- Many imaging studies lack diversity in ethnic and socioeconomic groups, limiting generalizability.
- Adjusting for maternal IQ reduces the IQ benefit to 2–3 points, fueling debate about causation.
- Modern formulas with DHA and ARA close the gap but can’t replicate breast milk’s live enzymes or HMOs.
Practical Steps for Parents:
- Try partial breastfeeding: Even 50% breast milk can improve gut-brain metabolites, supporting cognitive growth.
- Select nutrient-rich formulas: Choose formulas with DHA, ARA, and iron to mimic some of breast milk’s benefits according to Iron Deficiency Guide.
- Introduce brain-boosting solids at 6 months: Offer iron-rich cereals, pureed meats, or avocados to support brain growth as per Best First Foods.
- Engage in sensory play and reading: Activities like tummy time and reading aloud stimulate language acquisition and sensory development.
- Foster bonding: Use skin-to-skin contact and responsive feeding to replicate breastfeeding’s emotional benefits.
These steps can help parents support their baby’s brain development, regardless of feeding method.
Your Top Questions, Answered
-
Does partial breastfeeding still help?
Yes—any amount of breast milk boosts cognitive markers. Even mixed-fed infants show a healthier metabolome and higher test scores than formula-only peers. -
What’s the minimum duration for measurable brain benefits?
Three months of breastfeeding shows cognitive gains, with six months being optimal. Every week counts, and longer durations deepen the benefits. -
How does breastfeeding affect preterm babies?
It’s especially impactful, adding up to 8 IQ points by school age. Donor milk is a good alternative if mother’s milk isn’t available. -
Can advanced formulas match breast milk yet?
Not fully. While DHA and probiotics help, breast milk’s unique HMOs and live enzymes remain unmatched.
For more detailed comparisons, check the FAQ section at Breast Milk vs. Formula: What’s Best for Baby’s Brain?.
So, does breastfeeding really boost your baby’s brain?
The evidence—from MRI scans to long-term IQ studies—suggests that breastfeeding, particularly when exclusive and prolonged, offers meaningful cognitive benefits that can last into childhood. Pair breastfeeding with nutrient-dense foods from Brain-Boosting Foods, sensory play, and loving interaction to maximize your child’s neural potential.
Remember: every cuddle, every latch, and every drop of milk is a quiet vote for your baby’s brighter, more resilient mind.